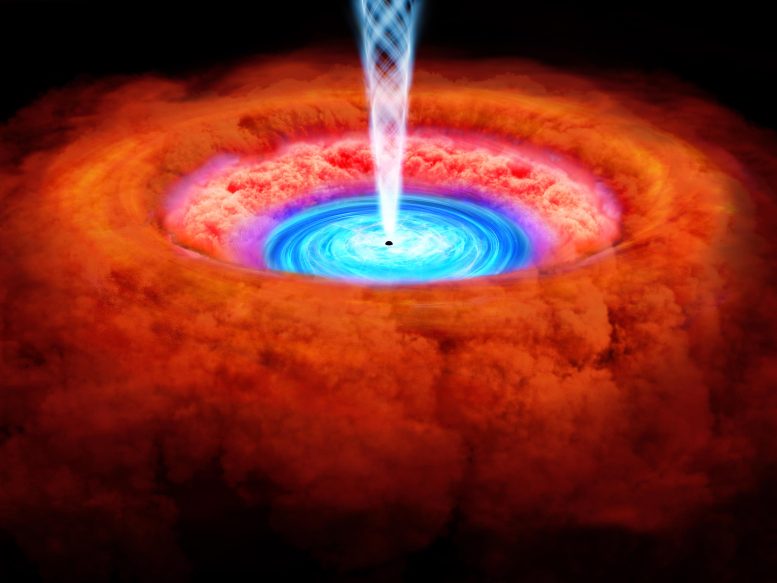
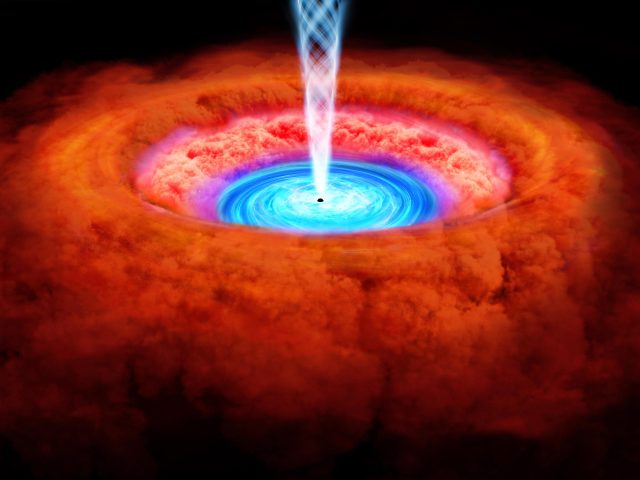
XRISM is transforming our understanding of supermassive black holes and their galactic neighborhoods, providing high-resolution X-ray spectra that reveal complex structures like twisted accretion disks.
This groundbreaking international space mission, a collaboration between JAXA, NASA, and ESA, is only beginning to unveil the intricate details of black holes and their impact on galaxy formation, with early data already confirming long-held hypotheses.
Initial data from an international space mission is confirming decades of hypotheses about the galactic environments surrounding supermassive black holes. Yet, even more thrilling is the satellite behind this data—the X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM)—is just getting started providing such unparalleled insights.
Unveiling the Mysteries of Supermassive Black Holes
“We have found the right tool for developing an accurate picture of the unexplored orders of magnitude around supermassive black holes,” Jon Miller, professor of astronomy at the University of Michigan, said of XRISM.
“We’re beginning to see clues of what that environment really looks like.”
The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency, or JAXA, which teamed up with NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) to create and launch XRISM, announced the new results on September 20.
The results were published on September 19 in two peer-reviewed studies, with Miller being the lead author of one accepted to The Astrophysical Journal Letters. He and more than 100 co-authors from around the world investigated what’s called an active galactic nucleus, which includes a supermassive black hole and its extreme surroundings.
To do this, they relied on XRISM’s unparalleled ability to gather and measure spectra of X-rays emitted by cosmic phenomena.
“It is truly exciting that we are able to gather X-ray spectra with such unprecedented high resolution, particularly for the hottest plasmas in the universe,” said Lia Corrales, U-M assistant professor of astronomy and a co-author of both XRISM publications.
“Spectra are so rich with information, we will surely be working to fully interpret the first datasets for many years to come.”
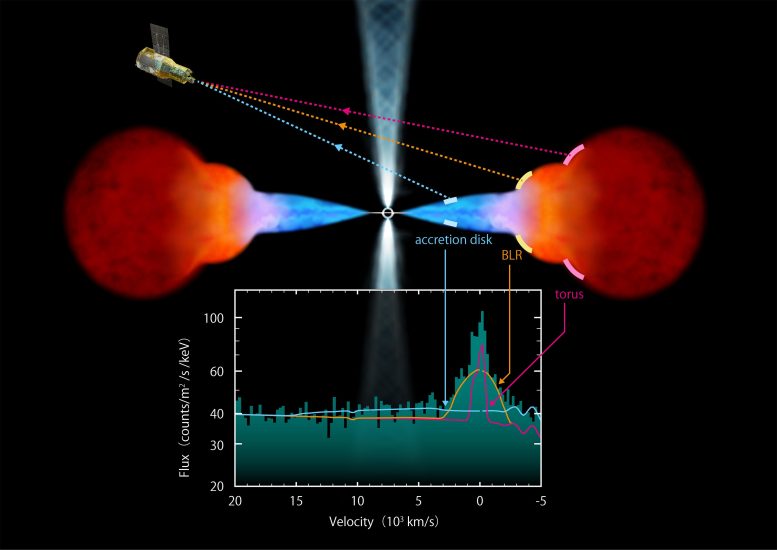
Exploring the Dynamics of Accretion Disks
Space exploration enthusiasts may know that the Chandra X-ray Observatory—what NASA calls its flagship X-ray telescope—recently celebrated its 25th anniversary of operating in space.
What’s less well known is that, over the past 25 years, an international cohort of scientists, engineers and space agency officials have been attempting to launch similarly sophisticated, but different X-ray missions.
The goal of these attempts was to provide high-quality, complementary data to better understand what Chandra and other telescopes were seeing. XRISM is now delivering that data.
With their data set, Miller, Corrales and their colleagues have solidified a hypothesis about structures called accretion disks near supermassive black holes in active galactic nuclei.
These disks can be thought of like vinyl records made of gas and other loose particles from a galaxy being spun by the spectacular gravity of the black holes at their centers. By studying accretion disks, researchers can better understand what’s happening around the black hole and how it impacts the lifecycle of its host galaxy.
By probing the center of a galaxy called NGC 4151, more than 50 million light-years away, the XRISM collaboration confirmed that the disk’s shape isn’t as simple as once thought.
“What we’re seeing is that the record isn’t flat. It has a twist or a warp,” Miller said. “It also appears to get thicker toward the outside.”
Although suggestions of this more complex geometry have emerged in other data over the past two and a half decades, the XRISM results are the strongest direct evidence for it.
“We had hints,” Miller said. “But somebody in forensics would say that we couldn’t have convicted anyone with what we had.”
The team also found that the accretion disk appears to be losing a lot of its gas. Again, scientists have theories about what happens to this material, but Miller said XRISM will enable researchers to find more definitive answers.
“It has been very hard to say what the fate of that gas is,” he said. “Actually finding the direct evidence is the hard work that XRISM can do.”
And XRISM isn’t just allowing researchers to think about existing theories in new ways. It’s enabling them to investigate parts of space that were invisible to them before.
Bridging the Gap in Black Hole Research
For all the talk of their gravitational pull being so strong that not even light can escape it, black holes are still responsible for creating a whole lot of electromagnetic radiation that we can detect.
For instance, the Event Horizon Telescope—a network of instruments on Earth sensitive to radiation emitted as radio waves—has enabled astronomers to zoom in and see the very edge of two different black holes.
There are other instruments on Earth and in space that detect different bands of radiation, including X-rays and infrared light, to provide larger, galaxy-scale views of the environs of black holes.
But scientists have lacked high-resolution tools to determine what was going on between those two scales, from right next to the black hole up to the size of its host galaxy. And that space between is where accretion disks and other interesting celestial structures exist.
If you were to divide the scale of the zoomed-out view of a black hole by that of its close-up, you’d get a number close to 100,000. To a physicist, each zero is an order of magnitude, meaning the gap in coverage spanned five orders of magnitude.
“When it comes to understanding how gas gets into a black hole, how some of that gas is lost and how the black hole impacts its host galaxy, it’s those orders of magnitude that really matter,” Miller said.
XRISM now gives researchers access to those scales by looking for X-rays emitted by iron around black holes and relying on the “S” in its acronym: spectroscopy.
Rather than using X-ray light to construct an image, XRISM’s spectroscopy instrument detects the energy of individual X-rays, or photons. Researchers can then see how many photons were detected with a particular energy across a range, or spectrum, of energies.
By collecting, studying and comparing spectra from different parts of the regions near a black hole, researchers are able to learn more about the processes afoot.
“We joke that spectra put the ‘physics’ in ‘astrophysics,’” Miller said.
Although there are other operational X-ray spectroscopy tools, XRISM’s is the most advanced and relies on a microcalorimeter, dubbed “Resolve.” This turns the incident X-ray energy into heat rather than, say, a more conventional electrical signal.
“Resolve is allowing us to characterize the multi-structured and multi-temperature environment of supermassive black holes in a way that was not possible before,” Corrales said.
XRISM provides researchers with 10 times better energy resolution compared with what they’ve had before, Miller said. Scientists have been waiting for an instrument like this for 25 years, but it hasn’t been for a lack of trying.
Persistent Pursuit of X-ray Spectroscopy Missions
Years before its 1999 launch, Chandra was initially conceived of as the Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility, a single mission that would fly with state-of-the-art technology for both X-ray imaging and spectroscopy.
That, however, proved to be too expensive, so it was divided into the Chandra telescope and a spectroscopy mission called Astro-E, whose development was led by JAXA. Unfortunately, Astro-E was lost during its launch in February 2000.
JAXA, NASA, and the European Space Agency all realized how important the tool was, Miller said, and worked together to essentially refly the Astro-E mission roughly five years later. This time, however, the mission was called Suzaku, named after a phoenix-like mythical bird.
“Suzaku made it into orbit, but its cryogenic system had a leak, so all its coolant leaked into space. Its prime scientific instrument never took actual data,” Miller said. “There was a different camera on board for X-rays, though, and it did really nice work for about 10 years.”
Within months of sunsetting Suzaku, the space agencies launched a third mission to provide the X-ray spectroscopy that the community was seeking. The mission took off as Astro-H in February 2016 and was renamed Hitomi after it entered orbit and deployed its solar panels.
Miller had traveled to Florida for a meeting about Hitomi right around the time disaster struck the mission. A maneuvering error sent Hitomi into an uncontrollable spin.
“It spun so fast that the solar panels flew off,” Miller said.
Less than 40 days after the launch, the space agencies lost contact with Hitomi.
“You could actually go out on the beach in Florida at night and watch it tumble across the sky,” Miller said. “It flickered in a very unique way.”
Before it ended, the Hitomi mission did manage to take what Miller quantified as one and a half scientific observations. That was enough to transform how researchers thought about galaxy clusters, which contain hundreds or thousands of galaxies, he said.
So it’s fair to say that a lot was riding on XRISM when it launched in September 2023. Based on early returns, it sounds like XRISM is equipped to deliver. Miller and a handful of his global colleagues were among the first to see the data that would lead to their new report.
“It was very late in Japan, an odd time in Europe and we were all on Zoom. All of us had trouble finding the words,” Miller said. “It was breathtaking.”
Miller’s original doctoral thesis project was meant to study data from the Astro-E mission, so he’s been invested for more than half his life and virtually his entire science career.
During that time, Hitomi and more successful missions like Chandra have been providing data that have enabled him and others in the field to further our understanding of the cosmos. But the researchers also knew they’d need something like the X-ray calorimeter on board XRISM to make the leaps they’ve been hungry for.
“It’s been difficult at many points, but we kept getting hints about what might be possible,” Miller said. “It’s almost impossible to replicate these environments in earthbound experiments and we’ve been wanting to know a lot of the details of how they really work. I think we’re finally going to make some progress on that.”
For more on these findings, see XRISM’s X-Ray Insights Uncover the Hidden Structures of Black Holes and Supernovas.
References:
“XRISM Spectroscopy of the Fe Kα Emission Line in the Seyfert Active Galactic Nucleus NGC 4151 Reveals the Disk, Broad-line Region, and Torus” by Marc Audard, Hisamitsu Awaki, Ralf Ballhausen, Aya Bamba, Ehud Behar, Rozenn Boissay-Malaquin, Laura Brenneman, Gregory V. Brown, Lia Corrales, Elisa Costantini, Renata Cumbee, Maria Diaz Trigo, Chris Done, Tadayasu Dotani, Ken Ebisawa, Megan E. Eckart, Dominique Eckert, Teruaki Enoto, Satoshi Eguchi, Yuichiro Ezoe, Adam Foster, Ryuichi Fujimoto, Yutaka Fujita, Yasushi Fukazawa, Kotaro Fukushima, Akihiro Furuzawa, Luigi Gallo, Javier A. García, Liyi Gu, Matteo Guainazzi, Kouichi Hagino, Kenji Hamaguchi, Isamu Hatsukade, Katsuhiro Hayashi, Takayuki Hayashi, Natalie Hell, Edmund Hodges-Kluck, Ann Hornschemeier, Yuto Ichinohe, Manabu Ishida, Kumi Ishikawa, Yoshitaka Ishisaki, Jelle Kaastra, Timothy Kallman, Erin Kara, Satoru Katsuda, Yoshiaki Kanemaru, Richard Kelley, Caroline Kilbourne, Shunji Kitamoto, Shogo Kobayashi, Takayoshi Kohmura, Aya Kubota, Maurice Leutenegger, Michael Loewenstein, Yoshitomo Maeda, Maxim Markevitch, Hironori Matsumoto, Kyoko Matsushita, Dan McCammon, Brian McNamara, François Mernier, Eric D. Miller, Jon M. Miller, Ikuyuki Mitsuishi, Misaki Mizumoto, Tsunefumi Mizuno, Koji Mori, Koji Mukai, Hiroshi Murakami, Richard Mushotzky, Hiroshi Nakajima, Kazuhiro Nakazawa, Jan-Uwe Ness, Kumiko Nobukawa, Masayoshi Nobukawa, Hirofumi Noda, Hirokazu Odaka, Shoji Ogawa, Anna Ogorzalek, Takashi Okajima, Naomi Ota, Stephane Paltani, Robert Petre, Paul Plucinsky, Frederick S. Porter, Katja Pottschmidt, Kosuke Sato, Toshiki Sato, Makoto Sawada, Hiromi Seta, Megumi Shidatsu, Aurora Simionescu, Randall Smith, Hiromasa Suzuki, Andrew Szymkowiak, Hiromitsu Takahashi, Mai Takeo, Toru Tamagawa, Keisuke Tamura, Takaaki Tanaka, Atsushi Tanimoto, Makoto Tashiro, Yukikatsu Terada, Yuichi Terashima, Yohko Tsuboi, Masahiro Tsujimoto, Hiroshi Tsunemi, Takeshi Tsuru, Hiroyuki Uchida, Nagomi Uchida, Yuusuke Uchida, Hideki Uchiyama, Yoshihiro Ueda, Shinichiro Uno, Jacco Vink, Shin Watanabe, Brian J. Williams, Satoshi Yamada, Shinya Yamada, Hiroya Yamaguchi, Kazutaka Yamaoka, Noriko Yamasaki, Makoto Yamauchi, Shigeo Yamauchi, Tahir Yaqoob, Tomokage Yoneyama, Tessei Yoshida, Mihoko Yukita, Irina Zhuravleva, Xin Xiang, Takeo Minezaki, Margaret Buhariwalla, Dimitra Gerolymatou and Scott Hagen, 19 September 2024, The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad7397
“The XRISM First Light Observation: Velocity Structure and Thermal Properties of the Supernova Remnant N132D” by XRISM Collaboration, 26 August 2024, Astrophysics > High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena.
arXiv:2408.14301




